Myeloma, also called multiple myeloma, is a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells, an important part of the immune system. This article explains what myeloma is, its causes, symptoms, and the treatments available, all in a simple and friendly tone.
What Is Myeloma?
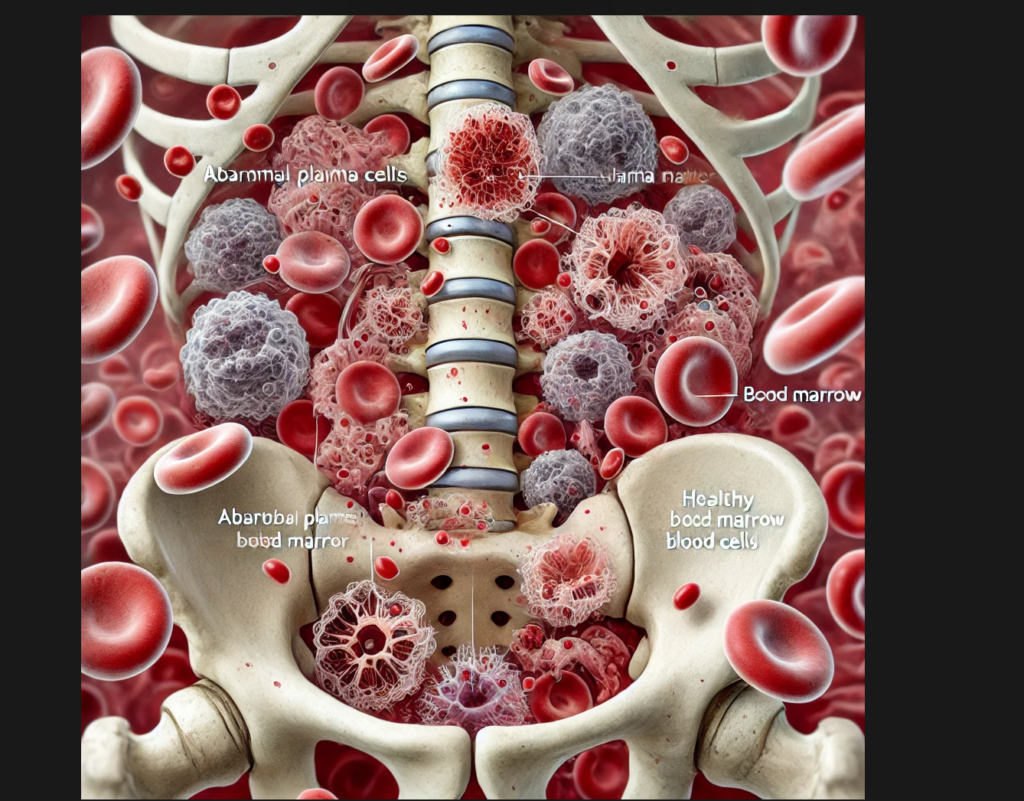
Myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells, which are found in the bone marrow. Plasma cells produce antibodies that help the body fight infections. In myeloma, these cells grow uncontrollably, crowding out healthy blood cells and producing abnormal proteins called monoclonal proteins (M proteins).
Types of Myeloma
Myeloma can be classified into several types based on the progression and behavior of the disease:
- Smoldering Myeloma: A slow-growing form that may not require immediate treatment.
- Active Myeloma: A more aggressive form causing symptoms like bone pain and kidney problems.
- Light Chain Myeloma: Produces only parts of antibodies (light chains), which can cause kidney damage.
What Causes Myeloma?
While the exact cause of myeloma is unknown, several factors may increase the risk:
- Age: Most cases occur in people over 60.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop myeloma than women.
- Race: In the USA, African Americans have a higher risk compared to other populations.
- Family History: A family history of myeloma or other blood cancers can increase the risk.
- Exposure to Toxins: Certain chemicals, like those used in farming or industrial work, may increase risk.
Symptoms of Myeloma
The symptoms of myeloma can vary widely but often include:
- Bone Pain: Especially in the spine or ribs, due to bone damage or fractures.
- Fatigue: Caused by anemia (low red blood cell count).
- Frequent Infections: Due to weakened immunity from abnormal plasma cells.
- Kidney Problems: Caused by the accumulation of M proteins.
- High Calcium Levels (Hypercalcemia): Leading to symptoms like nausea, confusion, and thirst.
Diagnosing Myeloma
1. Blood and Urine Tests
- Protein Electrophoresis: Identifies abnormal M proteins.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Detects anemia or low blood cell counts.
2. Imaging Tests
- X-rays, MRIs, or CT Scans: Reveal bone damage or tumors.
3. Bone Marrow Biopsy
A sample of bone marrow is examined to confirm the presence of myeloma cells.
Treatment Options for Myeloma
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the disease. Common options include:
1. Chemotherapy
Drugs are used to destroy myeloma cells and stop their growth.
2. Targeted Therapy
Medications like bortezomib and lenalidomide target specific proteins in myeloma cells.
3. Immunotherapy
Boosts the immune system to attack cancer cells. New therapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy, are showing promise in treating advanced cases.
4. Stem Cell Transplant
Healthy stem cells are transplanted to replace damaged bone marrow after high-dose chemotherapy.
5. Radiation Therapy
Focused radiation is used to relieve bone pain or shrink tumors.
Living with Myeloma in the USA
Myeloma is the second most common blood cancer in the USA, with over 35,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Advances in treatment have significantly improved survival rates.
“Early diagnosis and access to innovative treatments have made living with myeloma more manageable than ever before,” says Dr. Laura Kent, a hematologist in Boston.
Tips for Coping with Myeloma
- Stay Informed: Learn about your condition and treatment options.
- Seek Support: Join myeloma support groups or talk to a counselor.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help improve quality of life.
For detailed medical insights and resources, visit medicaltimes.io.
Top 10 FAQs About Myeloma
- What is the difference between myeloma and multiple myeloma?
Multiple myeloma is the most common type of myeloma, affecting multiple areas of the bone marrow. - Is myeloma curable?
While not curable, myeloma is highly treatable, and many patients live for years with proper care. - How is myeloma diagnosed?
Through blood tests, urine tests, imaging studies, and a bone marrow biopsy. - What are the early signs of myeloma?
Common early signs include fatigue, bone pain, and recurrent infections. - What is the life expectancy for someone with myeloma?
Survival varies based on the stage and response to treatment, but new therapies have greatly improved outcomes. - Can myeloma affect younger people?
While rare, myeloma can occur in people under 40. - What are the main complications of myeloma?
Bone fractures, kidney problems, and anemia are common complications. - Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage myeloma?
Yes, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding infections can improve well-being. - What are the side effects of myeloma treatments?
Side effects vary but may include fatigue, nausea, and increased infection risk. - Where can I find support for myeloma in the USA?
Many organizations, such as the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (MMRF), offer resources and support groups.
