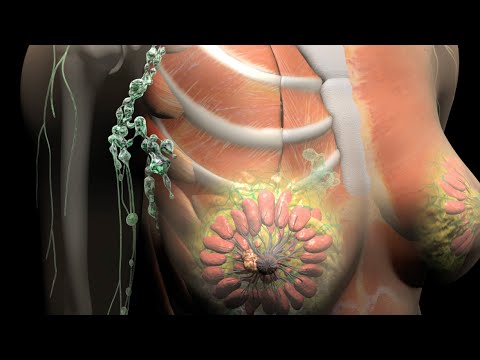
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers globally and a leading concern in women’s health, especially in the USA. With early detection and modern treatments, survival rates are improving, making awareness critical. This article provides a detailed overview of breast cancer, from risk factors to treatment options, with helpful insights for better understanding and prevention.
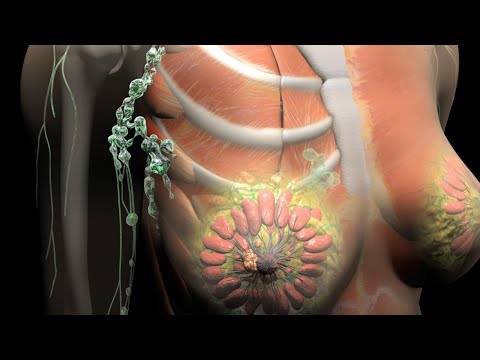
What Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast grow abnormally and uncontrollably, forming a lump or mass. While most cases originate in the milk ducts or lobules, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body if untreated.
Although women are predominantly affected, men can develop breast cancer too, though it’s much rarer.
Types of Breast Cancer
There are several types of breast cancer, broadly categorized into two groups:
1. Non-Invasive Breast Cancer
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): Affects the ducts and doesn’t spread beyond them.
- Highly treatable if caught early.
2. Invasive Breast Cancer
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): The most common type, spreading beyond the ducts into nearby tissue.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules) and can spread.
Other rare types include triple-negative breast cancer and HER2-positive breast cancer, which require specialized treatments.
How Common Is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide, excluding skin cancers. In the USA, it’s estimated that 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime. Early detection through mammograms has significantly improved outcomes.
What Are the Symptoms of Breast Cancer?
Recognizing early signs can save lives. Common symptoms include:
- A lump in the breast or underarm.
- Changes in breast size or shape.
- Dimpling or puckering of the skin.
- Nipple discharge, particularly if bloody.
- Redness, scaliness, or thickening of the skin.
- Pain or tenderness that doesn’t go away.
“If you notice changes in your breasts, even if minor, consult a healthcare provider promptly.”
Who Is at Risk for Breast Cancer?
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer:
1. Age
- Most cases are diagnosed in women over 50.
2. Family History
- Having a mother, sister, or daughter with breast cancer doubles the risk.
3. Genetic Mutations
- Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are strongly linked to breast cancer.
4. Hormonal Factors
- Early menstruation (before age 12) or late menopause (after age 55) increases risk.
- Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
5. Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity are linked to higher risk.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
How Is Breast Cancer Diagnosed?
Early detection improves survival rates significantly. Diagnostic tools include:
1. Mammogram
- A low-dose X-ray to detect abnormalities. Regular screenings are recommended for women over 40 in the USA.
2. Ultrasound or MRI
- Used to evaluate abnormalities detected during physical exams or mammograms.
3. Biopsy
- A sample of breast tissue is examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer.
Stages of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is staged based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and whether it has spread:
- Stage 0: Non-invasive, confined to ducts or lobules.
- Stage I-II: Early stages, limited spread.
- Stage III: Locally advanced but treatable.
- Stage IV: Metastatic, meaning cancer has spread to other organs.
Treatment Options for Breast Cancer
1. Surgery
- Lumpectomy: Removes only the tumor.
- Mastectomy: Removes the entire breast, sometimes both as a preventive measure.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Targets cancer cells with high-energy rays, often following surgery.
3. Chemotherapy
- Uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth.
- Often used for advanced or aggressive cancers.
4. Hormone Therapy
- Blocks hormones like estrogen that fuel some types of breast cancer.
5. Targeted Therapy
- Focuses on specific molecules, such as HER2 proteins, to stop cancer growth.
Prevention and Early Detection
While breast cancer cannot always be prevented, certain steps can reduce risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly and avoid smoking.
- Limit alcohol to one drink per day or less.
- Breastfeed if possible; it offers protective benefits.
- Get regular screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Life After Breast Cancer
Advances in treatment mean many people live full, healthy lives after breast cancer. Support groups, counseling, and lifestyle adjustments can aid recovery. Remember, early detection is key.
“Surviving breast cancer is not just about beating the disease but embracing life afterward with courage and resilience.”
For more insights on breast cancer and related health topics, visit medicaltimes.io.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the most common type of breast cancer?
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) is the most common. - At what age should I start mammograms?
In the USA, most women begin mammograms at age 40, but consult your doctor for personalized advice. - Is breast cancer always hereditary?
No, only about 5-10% of cases are linked to inherited genetic mutations. - Can men get breast cancer?
Yes, but it’s rare. Men account for less than 1% of breast cancer cases. - Does breastfeeding reduce breast cancer risk?
Yes, breastfeeding offers protective benefits by reducing lifetime exposure to estrogen. - What does triple-negative breast cancer mean?
It lacks estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors, making it harder to treat. - How is breast cancer staged?
Based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and spread to other organs. - Are all breast lumps cancerous?
No, many are benign, but any lump should be checked by a doctor. - Can diet affect breast cancer risk?
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help lower risk. - What is the survival rate for breast cancer?
It depends on the stage, but early-stage breast cancer has a 5-year survival rate of over 90%.