Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare but aggressive cancer that affects the bile ducts—small tubes carrying bile from the liver to the small intestine. Understanding this condition is essential for early detection and proper care. This article covers everything you need to know about bile duct cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Bile Duct Cancer?
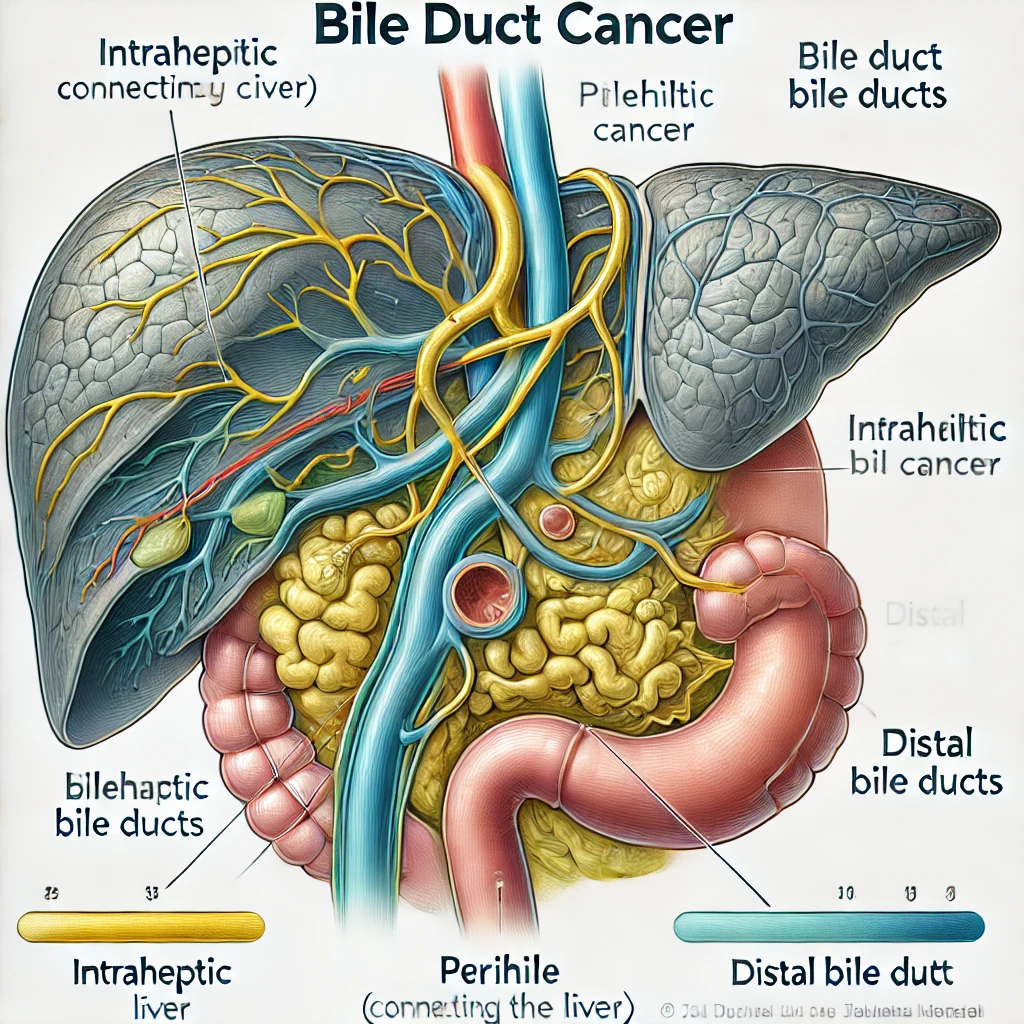
Bile duct cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the bile ducts. These ducts are crucial for digestion, as they transport bile, a fluid that helps break down fats. The disease can develop in various parts of the bile ducts, such as:
- Intrahepatic: Inside the liver.
- Perihilar (hilar): Near the liver’s exit.
- Distal: Closer to the small intestine.
What Causes Bile Duct Cancer?
While the exact cause is unknown, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing bile duct cancer.
Key Risk Factors:
- Chronic inflammation: Conditions like primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) may increase risk.
- Liver diseases: Hepatitis B or C infections.
- Parasitic infections: Liver flukes are common in some regions, although rare in the USA.
- Exposure to toxins: Chemicals like dioxins.
- Family history: Genetic predisposition may play a role.
Symptoms of Bile Duct Cancer
Symptoms can vary based on the tumor’s location but often include:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to bile buildup.
- Abdominal pain: Particularly in the upper right side.
- Dark urine and pale stools.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Itchy skin.
Early stages often show no symptoms, making routine check-ups critical for detection.
Diagnosing Bile Duct Cancer
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial. Doctors use several methods:
- Blood tests: To check liver function and tumor markers like CA 19-9.
- Imaging scans: Ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed images of the bile ducts.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Combines imaging with biopsy.
- Liver biopsy: Confirms cancer through a tissue sample.
Treatment Options for Bile Duct Cancer
Treatment depends on the cancer stage, location, and overall health of the patient. Common treatments include:
1. Surgery
- For early-stage cancers, removing the tumor may be possible.
- Complex surgeries like liver resection or bile duct removal may also be performed.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Used to shrink tumors or relieve symptoms in advanced cases.
3. Chemotherapy
- Drugs like gemcitabine and cisplatin are commonly used to kill cancer cells.
4. Targeted Therapy
- Focuses on specific cancer cell genes or proteins.
5. Liver Transplant
- In rare cases, a transplant may offer a cure, particularly for localized cancers.
Preventing Bile Duct Cancer
While not all cases are preventable, these tips can reduce your risk:
- Avoid liver infections: Vaccinate against hepatitis B and seek treatment for hepatitis C.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to several cancers.
- Limit alcohol intake: Excessive drinking can lead to liver disease.
- Avoid chemical exposures: Follow safety guidelines at work.
- Regular check-ups: Especially if you have a family history or chronic liver conditions.
Living with Bile Duct Cancer
Coping with bile duct cancer can be challenging, but support is available. Patients in the USA often benefit from:
- Cancer support groups: Many hospitals and organizations provide emotional support.
- Palliative care: Focuses on improving the quality of life during treatment.
- Financial resources: Organizations like the American Cancer Society help manage costs.
Visit Medicaltimes.io for More Insights
To explore detailed explanations, helpful tips, and in-depth information, visit medicaltimes.io.
Trusted Sources for Further Reading
Top 10 FAQs about Bile Duct Cancer
- What is bile duct cancer?
It’s a rare cancer affecting the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the intestine. - What are the first signs of bile duct cancer?
Jaundice, abdominal pain, and dark urine are common early signs. - Is bile duct cancer curable?
Early-stage cases may be treated with surgery, but advanced stages are harder to cure. - How is bile duct cancer diagnosed?
Blood tests, imaging scans, and biopsies are commonly used. - What are the survival rates for bile duct cancer?
Survival depends on the stage; localized cancers have better outcomes. - Who is at risk for bile duct cancer?
Risk factors include chronic liver disease, certain infections, and family history. - Can bile duct cancer spread?
Yes, it can metastasize to nearby organs like the liver and lymph nodes. - What is the most common treatment?
Surgery is most effective for localized cancers, followed by chemotherapy or radiation. - Can bile duct cancer be prevented?
While not always preventable, avoiding risk factors like infections and toxins can help. - Are there support groups for patients in the USA?
Yes, organizations like the American Cancer Society provide support groups and resources.