Endometrial cancer is the most common cancer of the female reproductive system, affecting the lining of the uterus, also known as the endometrium. In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about endometrial cancer, from its causes to available treatments, while emphasizing the importance of early detection and prevention.
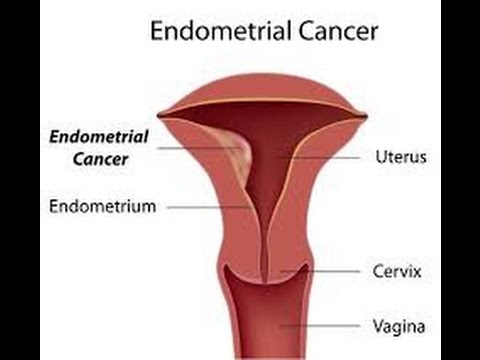
What is Endometrial Cancer?
Endometrial cancer develops when the cells in the lining of the uterus grow uncontrollably. It primarily affects postmenopausal women, though it can occur earlier.
The uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis, plays a vital role in reproduction. Any changes in the cells of its lining, like abnormal growth, can lead to cancer.
Common Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer
Recognizing symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment. Look out for these common signs:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: The most common symptom, especially after menopause.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort.
- Unusual vaginal discharge that may be watery or tinged with blood.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Unexplained weight loss.
In the USA, healthcare providers often emphasize the importance of consulting a doctor if any abnormal bleeding occurs.
Risk Factors for Endometrial Cancer
Some women are more at risk of developing endometrial cancer. Key factors include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Excess estrogen without enough progesterone can increase risk.
- Obesity: Extra fat tissue can increase estrogen levels.
- Age: Most cases occur in women over 50.
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes have a higher likelihood of developing endometrial cancer.
- Family History: A family history of cancers, like Lynch syndrome, raises risk.
“Understanding the link between lifestyle and health can make a significant difference,” said Dr. Amanda West, a women’s health specialist in the USA.
How is Endometrial Cancer Diagnosed?
Doctors use various tests to diagnose endometrial cancer:
- Pelvic Exam: To feel for abnormalities in the uterus and surrounding areas.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Provides a detailed image of the uterus and endometrial thickness.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken to detect cancer cells.
- Hysteroscopy: Allows doctors to look inside the uterus using a small camera.
Stages of Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is categorized into four stages:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the uterus.
- Stage II: It has spread to the cervix but not beyond.
- Stage III: Cancer has reached nearby structures like the vagina or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: It has metastasized to distant organs, such as the bladder or lungs.
Treatment Options for Endometrial Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer and overall health of the patient. The most common options include:
- Surgery:
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, often with nearby lymph nodes.
- Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: Removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Hormonal Therapy: Recommended for advanced cases, especially when cancer is estrogen-sensitive.
- Chemotherapy: Used in advanced stages to target cancer cells throughout the body.
- Immunotherapy: A newer approach that boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
Can Endometrial Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all cases are preventable, certain lifestyle changes can reduce risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a significant risk factor.
- Be active: Regular exercise helps regulate hormones.
- Manage conditions like diabetes effectively.
- Use birth control pills: They can reduce the risk when used long-term.
- Attend regular check-ups: Early detection improves outcomes significantly.
For more health tips and preventative measures, visit medicaltimes.io.
Living with Endometrial Cancer
Receiving a diagnosis of endometrial cancer can feel overwhelming, but many women successfully overcome it with treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Support groups, counseling, and family involvement play crucial roles in emotional recovery.
3 Trusted Resources for Endometrial Cancer Information
- American Cancer Society: https://www.cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute: https://www.cancer.gov
- Foundation for Women’s Cancer: https://www.foundationforwomenscancer.org
- Endometrial cancer – Symptoms and causes
- Womb Cancer (Endometrial Cancer / Uterine Cancer) – NCIS
- Endometrial Cancer Treatment – NCI
- Uterine Cancer (Endometrial Cancer) – Cleveland Clinic
- What Is Endometrial Cancer? | Types of …
Top 10 FAQs About Endometrial Cancer
- What is the main cause of endometrial cancer?
Hormonal imbalances, especially excess estrogen, are primary causes. - Who is at risk of endometrial cancer?
Postmenopausal women, those with obesity, or a family history are at higher risk. - How is endometrial cancer treated?
Treatment involves surgery, radiation, hormonal therapy, or chemotherapy. - Can endometrial cancer occur before menopause?
Yes, but it is more common in postmenopausal women. - What are the survival rates for endometrial cancer?
Early-stage cancers have a high survival rate, often exceeding 90%. - Does endometrial cancer spread quickly?
The rate of spread depends on the type and stage of cancer. - Is endometrial cancer hereditary?
Certain genetic conditions, like Lynch syndrome, increase risk. - How can I prevent endometrial cancer?
Maintain a healthy weight, exercise, and attend regular check-ups. - What tests diagnose endometrial cancer?
Biopsies, ultrasounds, and hysteroscopies are commonly used. - Can I have children after endometrial cancer treatment?
Fertility may be affected, especially after a hysterectomy, but options like surrogacy exist.
