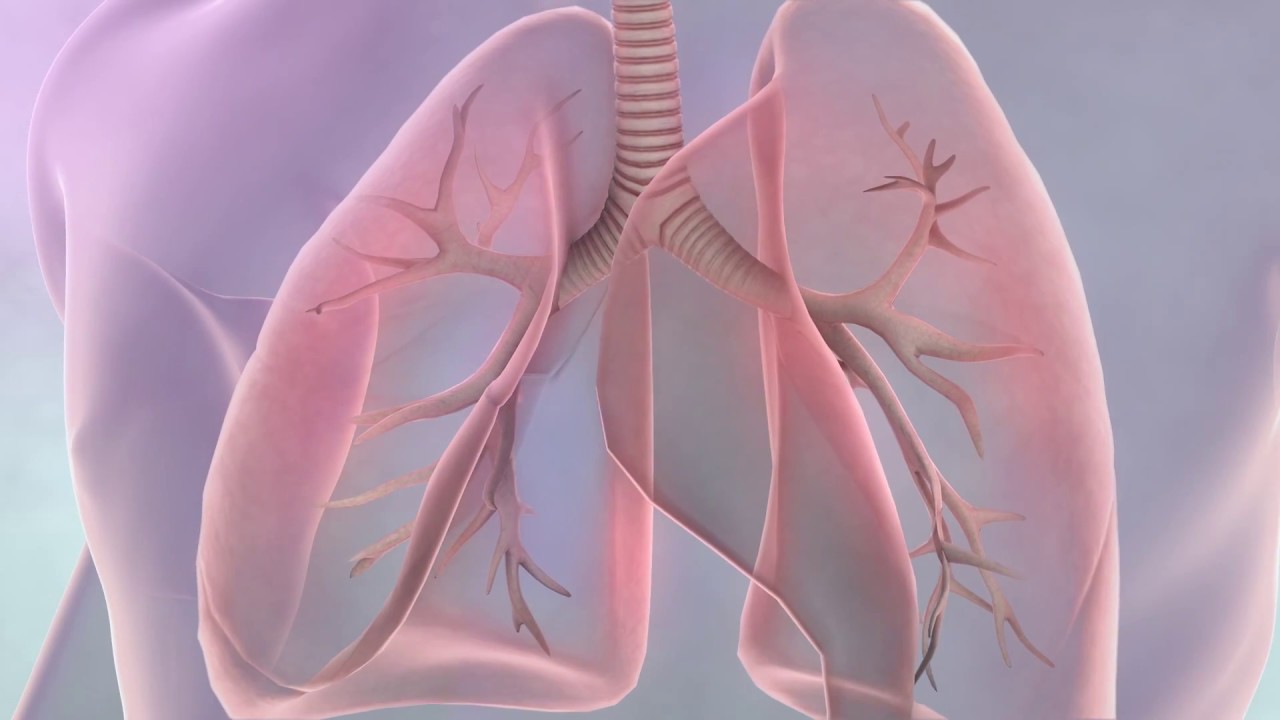
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent and life-threatening cancers globally, especially in the USA. This disease, often linked to smoking but also affecting non-smokers, demands awareness and early intervention. This article breaks down lung cancer in an easy-to-read format, covering everything from causes to treatments.
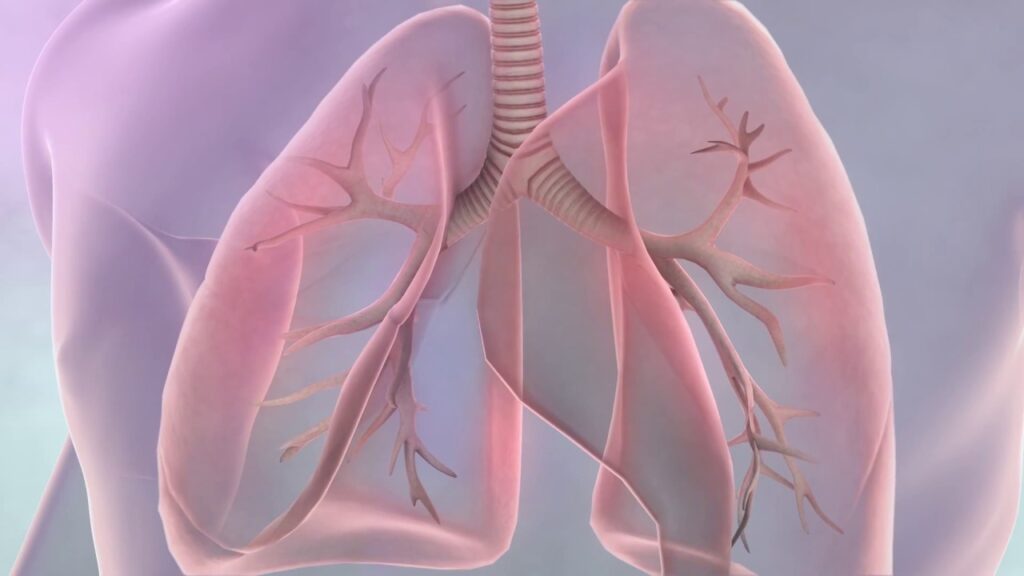
What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer begins when cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that interfere with normal lung function. These tumors may spread to other parts of the body (metastasis), making early detection crucial.
Types of Lung Cancer
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- The most common type, accounting for about 85% of cases.
- Includes subtypes like adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- Less common but more aggressive.
- Often spreads quickly to other parts of the body.
How Common Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is the second most diagnosed cancer in the USA. According to the American Cancer Society, over 230,000 new cases are reported annually. Sadly, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths, highlighting the importance of awareness and prevention.
What Causes Lung Cancer?
While smoking is the primary cause, other factors also play a role:
1. Smoking
Cigarette smoking accounts for 80-90% of lung cancer cases, with both smokers and those exposed to secondhand smoke at risk.
2. Radon Gas
A naturally occurring gas that can seep into homes and buildings, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers.
3. Air Pollution
Prolonged exposure to pollutants, including industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust, can increase the risk.
4. Occupational Hazards
Jobs involving asbestos, arsenic, or diesel exhaust exposure also raise the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Early-stage lung cancer often has no symptoms, but as it progresses, the following may occur:
- Persistent cough that worsens over time.
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum.
- Shortness of breath or wheezing.
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Hoarseness or voice changes.
- Fatigue and loss of appetite.
“Don’t ignore a persistent cough or breathing issues. Early detection can save lives.”
How Is Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
1. Imaging Tests
- X-rays and CT scans reveal abnormalities in the lungs.
- PET scans help determine if cancer has spread.
2. Biopsy
A sample of lung tissue is examined to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
3. Bronchoscopy
A thin tube with a camera examines the airways and collects tissue samples.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is classified into stages based on its spread:
- Stage 1: Limited to the lungs.
- Stage 2: Spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Spread to distant lymph nodes or nearby organs.
- Stage 4: Spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver or bones.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
Treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health. The main options include:
1. Surgery
Used to remove tumors when the cancer is localized. Common procedures include lobectomy (removing a lung lobe) or pneumonectomy (removing an entire lung).
2. Radiation Therapy
High-energy beams target and destroy cancer cells, often used with surgery or for inoperable cases.
3. Chemotherapy
Drugs that kill rapidly growing cells are delivered orally or intravenously.
4. Targeted Therapy
Specific drugs like EGFR inhibitors target genetic mutations in cancer cells, sparing healthy cells.
5. Immunotherapy
Boosts the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Living with Lung Cancer
Lung cancer treatment can be challenging, but advancements in therapies offer hope. Support groups, counseling, and proper nutrition can improve quality of life during and after treatment.
“Every step you take is a step toward hope and healing.”
Preventing Lung Cancer
While not all cases are preventable, these steps can reduce your risk:
- Quit smoking or avoid starting.
- Test your home for radon levels.
- Avoid exposure to asbestos and carcinogens.
- Wear protective gear if working in hazardous environments.
- Stay active and eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
For more health insights and tips, visit medicaltimes.io. Stay informed and empowered to make the best decisions for your health.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can non-smokers get lung cancer?
Yes, radon gas, air pollution, and genetic factors can cause lung cancer in non-smokers. - What is the most common symptom of lung cancer?
A persistent cough is the most common early sign. - How is lung cancer detected early?
Low-dose CT scans are recommended for high-risk individuals, such as heavy smokers. - What is the survival rate for lung cancer?
Early-stage lung cancer has a 5-year survival rate of about 60%, but this drops in later stages. - Is lung cancer curable?
It can be curable if detected early and treated appropriately. - Does quitting smoking reduce lung cancer risk?
Yes, quitting smoking significantly lowers your risk over time. - What are the side effects of chemotherapy for lung cancer?
Common side effects include nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. - Can children develop lung cancer?
While rare, lung cancer can occur in children due to genetic factors or exposure to carcinogens. - How long does lung cancer treatment take?
Treatment duration varies but often spans several weeks to months, depending on the therapy. - What is palliative care in lung cancer?
Palliative care focuses on improving quality of life by managing symptoms and providing emotional support.
Reference :
Lung cancer – Symptoms and causes
Lung Cancer: Types, Stages, Symptoms, Diagnosis & …
Lung Cancer – Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Lung Cancer – Causes, Symptoms & Treatments