Kidney cancer is one of the most common cancers in adults, and its early diagnosis plays a crucial role in effective treatment. In this comprehensive article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about kidney cancer, from what it is to how it’s treated.
What is Kidney Cancer?
Kidney cancer occurs when cells in the kidneys grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The most common type is renal cell carcinoma (RCC), making up about 90% of cases.
The kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back, are essential for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid balance. When cancer affects them, it disrupts these critical functions.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
Recognizing the early warning signs of kidney cancer can save lives. Common symptoms include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Persistent pain in the side or lower back
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever that isn’t caused by an infection
Sometimes, kidney cancer is detected incidentally during imaging tests for other health issues, especially in the USA, where regular health screenings are emphasized.
Risk Factors for Kidney Cancer
Some people are at a higher risk of developing kidney cancer. Key factors include:
- Smoking: Increases the risk by up to 50%.
- Obesity: Excess weight places added stress on the kidneys.
- High blood pressure: Also known as hypertension, it’s a significant contributor.
- Genetics: Family history or conditions like von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
- Exposure to harmful substances: Industrial chemicals and toxins like cadmium.
As Dr. David Small from the USA once said, “Understanding your risk factors can empower you to take preventive steps for better health.”
How is Kidney Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of the following tests:
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed views of the kidneys.
- Blood and Urine Tests: To assess kidney function and check for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A small sample of kidney tissue may be examined to confirm cancer.
These methods help doctors determine the stage of cancer, which influences treatment options.
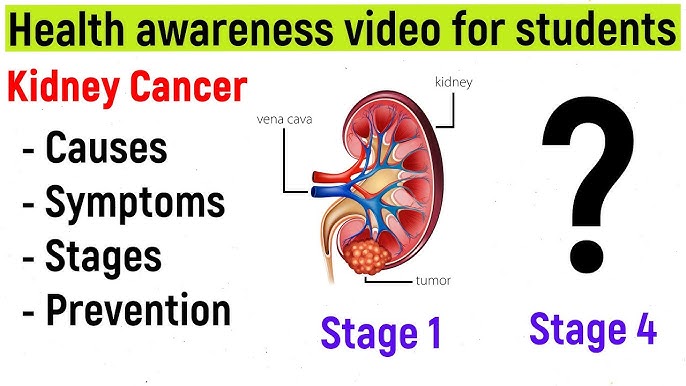
Stages of Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer stages range from I to IV:
- Stage I: Tumor is small and confined to the kidney.
- Stage II: Larger tumor but still limited to the kidney.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or blood vessels.
- Stage IV: Cancer has metastasized to other organs.
Early detection often leads to better outcomes, so regular check-ups are vital.
Treatment Options for Kidney Cancer
The treatment approach depends on the stage and overall health of the patient. Common treatments include:
- Surgery:
- Partial nephrectomy: Removes the tumor while sparing the kidney.
- Radical nephrectomy: Removes the entire kidney.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used for advanced cases or palliative care.
- Active Surveillance: In some cases, especially in older adults or those with small, slow-growing tumors, careful monitoring may be recommended.
Can You Prevent Kidney Cancer?
While not all cases can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by adopting a healthier lifestyle:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation greatly lowers your risk.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise promotes overall kidney health.
- Control Blood Pressure: Monitor and manage hypertension effectively.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on fresh vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins.
Living with Kidney Cancer
A diagnosis of kidney cancer can feel overwhelming, but many people live full, meaningful lives post-treatment. Joining a support group, maintaining a positive outlook, and focusing on follow-up care are key steps in managing your health.
For additional resources and tips, visit medicaltimes.io.
3 Trusted Resources for Kidney Cancer Information
- American Cancer Society: https://www.cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute: https://www.cancer.gov
- Kidney Cancer Association: https://www.kidneycancer.org
Top 10 FAQs About Kidney Cancer
- What are the early signs of kidney cancer?
Blood in the urine, back pain, and unexplained weight loss are common signs. - Who is at risk for kidney cancer?
People who smoke, are obese, or have high blood pressure are at higher risk. - How is kidney cancer treated?
Treatments include surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. - Is kidney cancer hereditary?
Some cases are linked to genetic conditions like von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. - Can kidney cancer be cured?
Yes, especially when caught in the early stages. - What lifestyle changes can reduce risk?
Quit smoking, stay active, and maintain a healthy weight. - Does kidney cancer affect both kidneys?
It usually affects one kidney, but rare cases involve both. - Are there any new treatments available?
Yes, advances in targeted and immunotherapy are promising. - What should I eat if I have kidney cancer?
A balanced diet with limited sodium and protein is recommended. - How often should I see my doctor after treatment?
Regular follow-ups are crucial, typically every 6-12 months.
