Melanoma is a type of cancer that starts in melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which gives skin its color. Although less common than other skin cancers, melanoma is far more aggressive and can spread rapidly if untreated.
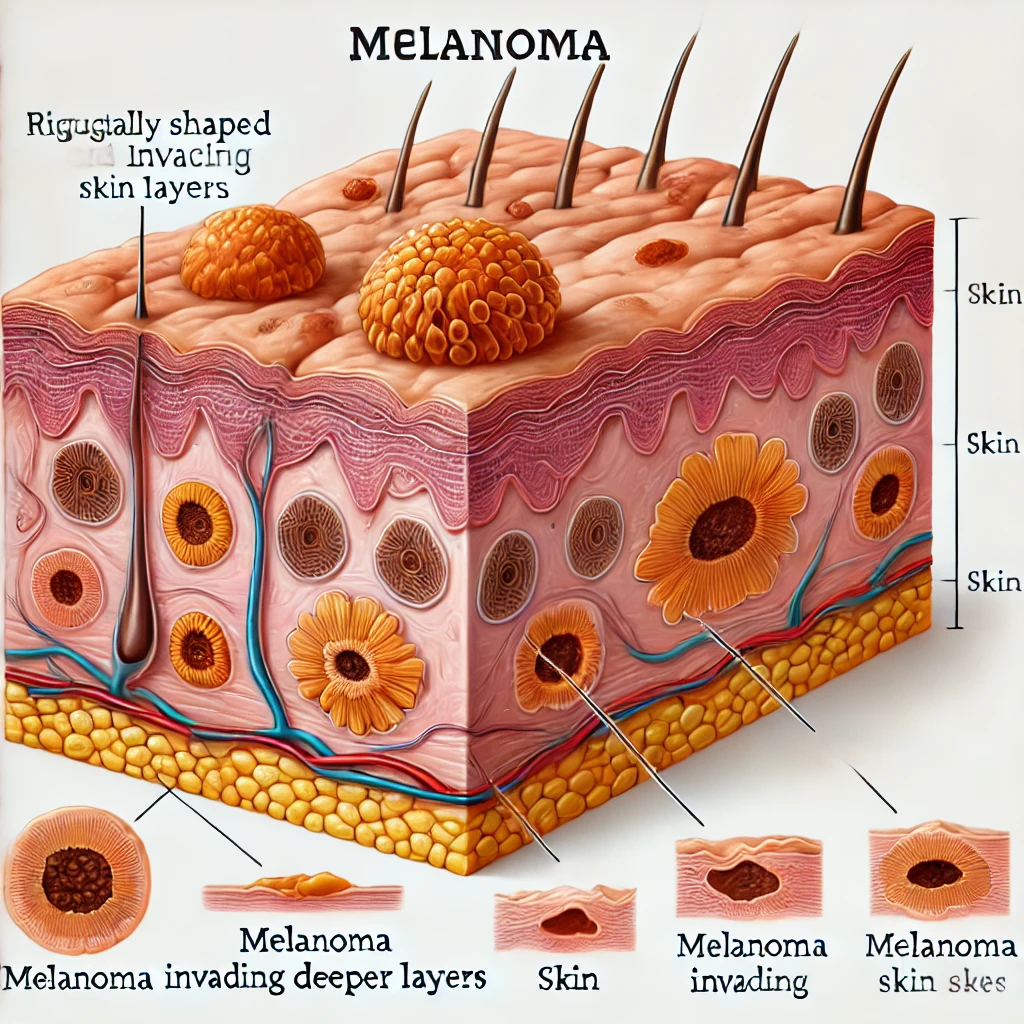
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma occurs when melanocytes mutate and grow uncontrollably. It often appears as an irregular mole or pigmented patch on the skin but can also develop in areas not exposed to the sun, like the soles of the feet, palms, or under nails.
How Melanoma Develops
- UV Radiation: Most melanomas are caused by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of melanoma significantly increases the risk.
- Pre-existing Moles: Changes in moles can signal melanoma.
Early Signs of Melanoma: The ABCDE Rule
Early detection is crucial. Use the ABCDE rule to identify suspicious moles:
- A: Asymmetry – One half doesn’t match the other.
- B: Border – Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges.
- C: Color – Uneven shades of black, brown, red, or white.
- D: Diameter – Larger than a pencil eraser (6 mm).
- E: Evolving – Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
- Excessive Sun Exposure
People living in sunny regions, such as parts of the USA like Florida and California, have a higher risk. - Use of Tanning Beds
The World Health Organization classifies tanning beds as a significant risk factor for melanoma. - Fair Skin
Individuals with light skin, freckles, or red hair are at greater risk due to less natural UV protection. - Family History
A close relative with melanoma can double your chances of developing it. - Weakened Immune System
Those undergoing organ transplants or with conditions like HIV/AIDS are more vulnerable.
Diagnosing Melanoma
1. Skin Examination
Dermatologists check for abnormal moles or lesions during routine exams.
2. Dermoscopy
A dermatoscope magnifies skin structures, helping identify suspicious features.
3. Biopsy
A sample of the affected tissue is analyzed under a microscope to confirm melanoma.
Treatment Options for Melanoma
1. Surgical Removal
Early-stage melanomas are often treated by removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin.
2. Immunotherapy
Drugs like checkpoint inhibitors boost the immune system to fight cancer.
3. Targeted Therapy
For melanomas with specific mutations (like BRAF), targeted drugs can halt growth.
4. Radiation Therapy
Used for advanced melanomas or to relieve symptoms.
5. Chemotherapy
Rarely the first choice, chemotherapy may be used if other treatments fail.
Prevention Tips for Melanoma
1. Use Sunscreen Daily
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Apply generously and reapply every two hours.
2. Avoid Tanning Beds
Artificial UV radiation poses significant melanoma risks.
3. Wear Protective Clothing
Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses can protect your skin.
4. Seek Shade
Avoid outdoor activities during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
5. Regular Skin Exams
Check your skin monthly for changes and consult a dermatologist annually.
Living with Melanoma
Surviving melanoma means lifelong vigilance. Regular follow-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of recurrence. Emotional support, whether through counseling or support groups, can be invaluable.
For more advice, visit medicaltimes.io.
Top 10 FAQs About Melanoma
1. What is melanoma?
Melanoma is a skin cancer originating from melanocytes, often caused by UV exposure or genetic factors.
2. How common is melanoma in the USA?
Over 100,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with increasing rates in young adults.
3. Can melanoma be cured?
Early-stage melanoma is highly treatable. Advanced melanoma requires aggressive treatment but can still have positive outcomes.
4. What are the first signs of melanoma?
Irregular moles that change in size, color, or shape are common early signs.
5. Are tanning beds safe?
No, tanning beds are a significant risk factor for melanoma and should be avoided.
6. How often should I see a dermatologist?
At least once a year for a professional skin exam.
7. Can dark-skinned individuals get melanoma?
Yes, though less common, melanomas in darker skin tones often appear in less exposed areas like the palms or soles.
8. How do I perform a self-skin check?
Examine your skin monthly in front of a mirror, checking hard-to-see areas like the back and scalp.
9. Is melanoma hereditary?
Yes, having a family history of melanoma increases your risk.
10. What is the survival rate for melanoma?
When detected early, the five-year survival rate is over 90%.
