The Extreme Fasts of David Blaine and Angus Barbieri
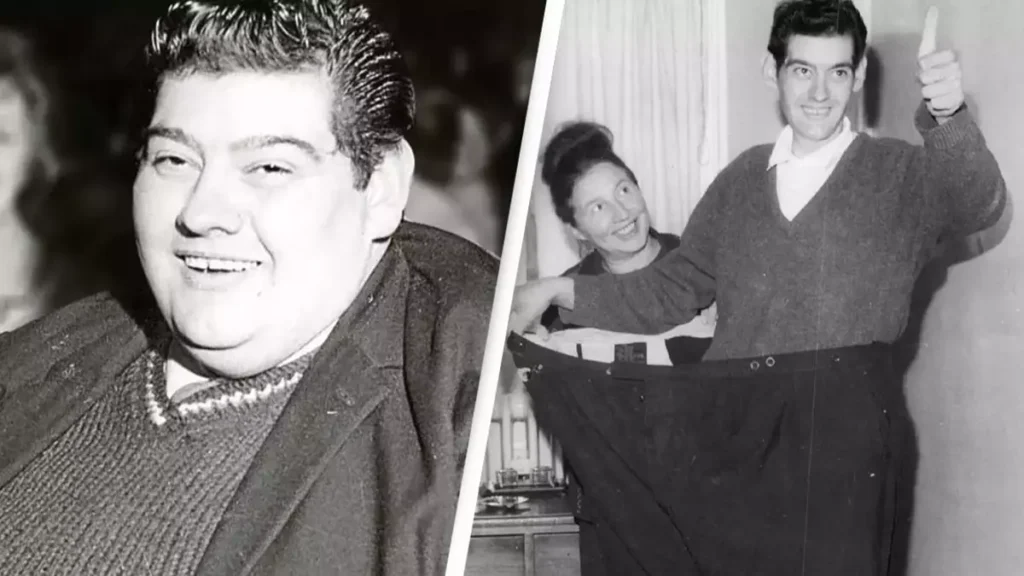
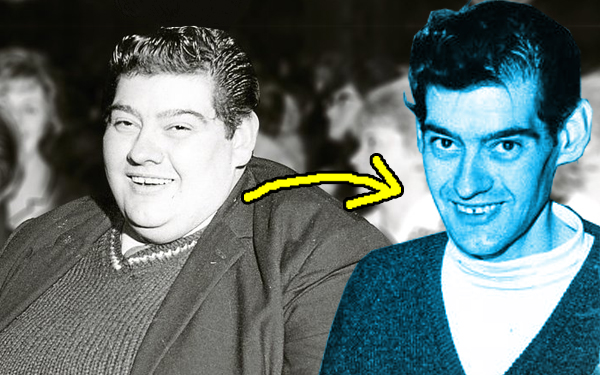
In 2003, magician David Blaine captured public attention by fasting for 44 days while suspended in a transparent box over the Thames River in London. Blaine claimed, “I also didn’t go to the bathroom for a month and a half.” This feat, however, is eclipsed by Angus Barbieri, who holds the record for the longest fast: 382 days without food.
What Happens to the Body During Extended Fasting?
Fasting has gained popularity for its potential health and cognitive benefits. But what really happens to our body when we stop eating?
- Initial Fasting Phase (0-48 Hours)
- After about 8 hours without food, the body begins to deplete its liver’s stored glucose for energy, leading to increased hunger.
- Growth hormone levels rise significantly, while the hunger hormone ghrelin decreases.
- After 48 hours, Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), a protein crucial for brain growth, increases by 3.5 times.
- Longer Fasting (72+ Hours)
- At around 72 hours, insulin levels drop significantly, signaling the body to start burning fat for energy.
- The body begins producing ketones, an alternative fuel source that meets about two-thirds of the brain’s energy needs during fasting.
Ketones and Brain Function
Ketones are not just a substitute for glucose; they provide a more efficient energy source for the brain. They promote brain growth by increasing BDNF, enhancing cognitive function, and improving mood.
Emotional and Physical Effects of Fasting
Surprisingly, many people report improved emotional well-being during fasting. A study of 1,422 participants found that feelings of anxiety and depression often improved after several days of fasting. Participants reported increased focus and energy, with 93% stating their hunger decreased after three days.
The Risks of Prolonged Fasting
While there are benefits to fasting, extreme fasting carries risks:
- Blaine experienced adverse effects such as heart palpitations and blurred vision during his 44-day fast. He lost 54 lbs, with 42.4% of that being muscle mass.
- Long fasts can lead to muscle breakdown, particularly if physical activity is restricted. Staying active can mitigate some muscle loss.
Health Benefits of Short and Long Fasts
Research shows fasting can have significant health benefits:
- Participants in a fasting study reported improvements in health issues, including diabetes and arthritis.
- Angus Barbieri’s 382-day fast was notably uneventful, and he managed to maintain his weight loss after refeeding.
Conclusion: Fasting Can Be Safe, But Should Be Done Carefully
While fasting can have health benefits, it’s important to approach it cautiously, especially for extended periods. Ensuring proper electrolyte balance during fasting can help prevent fatigue and other negative symptoms. If you’re considering fasting, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional and take a gradual approach.
A Note on Electrolytes
During fasting, insulin levels drop, causing the kidneys to excrete more electrolytes. Supplementing with electrolytes can help maintain energy levels and overall well-being during fasting.
Fasting can be a powerful tool for health improvement, but like all things, moderation and proper guidance are key.
Angus barbieri last photo
angus barbieri last photo